1. The main characteristics of desulfurization wastewater from coal-fired power plants
Characteristics of desulfurization wastewater from coal-fired power plants:
(1) High salt content. In desulfurization wastewater, due to the change of power generation intensity, the salt content is often higher than other impurities, and the salt content per liter of wastewater is between 30,000-600,000 mg, and the salt content is large. It will increase the difficulty and cost of processing.
(2) The composition is complex and the water quality changes greatly.
(3) High suspended solids content.
2. The existing zero discharge technology of desulfurization wastewater in coal-fired power plants
(1) Flue spray drying technology.
Desulfurization wastewater is pumped into the flue in front of the dust collector. The desulfurization wastewater is delivered into the flue gas by means of compressed air through a fixed atomization nozzle. The flue gas temperature is used to dry the droplets and collect various solids in the wastewater, which are collected by the dust collector. The process is simple, the investment, operation and management costs are relatively low, and there are few foreign application results, and there are no successful operation cases in our country, and it is still in the trial stage or has not yet been implemented. Flue gas clogging, wear, corrosion and flue gas temperature caused by sewage need to be tested in practice.
(2) Pretreatment - traditional evaporation crystallization.
Desulfurization wastewater removes most of the suspended solids, heavy metals, and scaling substances such as F-, hardness, and SiO2 by adding lime (sodium carbonate), organic sulfur, flocculants, and gravity sedimentation. It is evaporated and crystallized by a multi-effect evaporator or mechanical steam recompression evaporator, reused by condensate, and treated with crystallization salt. The technology is mature and reliable, but the investment and operating costs are high.
(3) Pretreatment - membrane concentration - traditional evaporation and crystallization.
After pretreatment with lime (sodium carbonate), flocculant and gravity settling, most of the suspended solids, heavy metals and scaling substances such as F-, hardness and SiO2 were removed from the desulfurization wastewater. On this basis, the pretreated wastewater is concentrated by using open channel reverse osmosis membrane-coil reverse osmosis membrane, nanofiltration - special channel reverse osmosis membrane, forward osmosis membrane, etc., and the fresh water is reused, and the concentrated water enters the traditional evaporation crystallization system. The condensate is reused and the crystalline salts are treated separately.
3. Analysis of the characteristics of the softening process of five pretreatments
Although the desulfurization wastewater was treated with three vessels, the hardness, suspended solids, SiO2, Fe, and HCO3 concentrations of subsequent membrane treatment were still very high, so the softening pretreatment still needed to be strengthened. After pretreatment, the effluent quality meets the requirements of the membrane inlet before it can enter the membrane system to achieve the purpose of concentration and reduction of water volume. There are two main schemes for desulfurization wastewater softening pretreatment.
(1) Lime (or caustic soda-sodium carbonate) softening process.
Lime (or caustic soda-sodium carbonate) softening has been widely used in the softening treatment of wastewater. This process has the advantages of stability and reliability. For example, the softening of wastewater in a power plant can reduce the total hardness of the two-stage chemical softening treatment to less than 100ppm. After adjusting the pH to the evaporation system, the stable operation of the evaporation system can be ensured. The disadvantage of this process is that it consumes a lot of chemicals and produces a lot of sludge during the softening process. At the same time, the cost of sludge treatment will also increase.
(2) Ion exchange softening process.
Stability and reliability are the process characteristics of this system. After ion exchange, the hardness of the effluent can be reduced to less than 10ppm, but the hardness of desulfurization wastewater is too high, and there are problems such as excessive equipment investment and excessive output of recycled wastewater. Therefore, in practical applications, it is possible to consider increasing ion exchange softening in chemically softened wastewater to further reduce the hardness of wastewater and ensure the stable operation of subsequent systems. A small amount of recycled wastewater can be returned to the original chemical softening system to ensure that the system does not produce new pollutants to achieve the system's "zero discharge" effect.
(3) Sodium sulfate-lime-flue gas softening process.
The main principle of sodium-lime flue gas softening process is that the dissolution of Ca(OH)2 in the three-phase CaSO4-Ca(OH)2-H2O system affects the solubility of CaSO4. The process can be divided into two steps: adding sodium sulfate and lime emulsion, adjusting the pH value to 12~13, precipitating gypsum particles; In the second step, the desulfurization flue gas is introduced into the wastewater after the first step of treatment, and CO2 is added to the flue gas. It reacts with OH- in wastewater to form CO32-, and then combines with Ca2+ in wastewater to form calcium carbonate precipitate, removing calcium ions and controlling pH at about 11. The advantage of this method is that it can reduce the cost of pretreatment softener, but the pH value of the softening process is difficult to control, and it is difficult to achieve a good softening effect.
(4) Nanofiltration membrane as a softening pretreatment process.
In the process of desalination pretreatment, nanofiltration membrane is used as the softening pretreatment process. Nowadays, there are many softening nanofiltration membranes in industry, but their hardness removal rate does not exceed 50%. Concentrated nanofiltration water still needs to be treated. Due to membrane clogging and contamination, there is currently no "zero discharge" process applied to desulfurization wastewater.
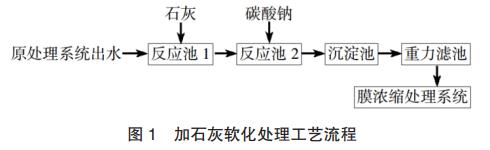
(5) Lime-sodium carbonate softening-sedimentation tank-filter treatment process.
The effluent from the desulfurization wastewater treatment system of the coal-fired power plant enters reactor 1 and reactor 2 in turn, and a certain amount of lime and sodium carbonate are added to the two reaction tanks respectively. Its main purpose is to use the chemical reaction of magnesium and calcium ions in wastewater to produce precipitation, and then separate the solid and liquid in the sedimentation tank. After precipitation, the supernatant can be filtered by filtration and ultrafiltration. In membrane concentration treatment systems, the effluent is used directly as influent water. The process of softening with lime is shown in Fig. 1.
4. Conclusions and suggestions
Sum up:
(1) Flue spray drying technology, pretreatment-traditional evaporation crystallization technology, pretreatment-membrane concentration-traditional evaporation crystallization, etc. are the most basic zero-discharge treatment processes for desulfurization wastewater.
(2) According to the industry requirements of the pretreatment process, we have introduced various types of processes such as lime (or caustic soda-sodium carbonate) softening, which can be selected by power enterprises according to actual needs.





















